What Makes for Good View for Conrastive Learning?
Yonglong Tian et al. NIPS 2020
c. https://arxiv.org/pdf/2005.10243
https://github.com/HobbitLong/PyContrast
Main point in this paper
• reducing the mutual information(MI)
• keeping task-relevant in formation
위를 만족 시킬 수 있는 View 찾기 → InfoMin Principle
3.1 Multiview Contrastive Learning

MI량 >= K개의 방해 요소에 따른 상수 - InfoNCE 손실함수 = MI량의 하한
3.2 Three Regimes of Information Captured - InfoMin Principle
⁕ Missing information - I(v1;v2) < I(x;y), there is information about task-relevant
⁕ Sweet spot - I(v1;y)= I(v2;y)= I(v1;v2)= I(x;y), the only information shared between v1 and v2 is task-relevant
⁕ Excess noise - include additional information that is irrelevant

<InfoMin Principle>
• reducing the Mutual Information(MI) - removing task-irrelevant information

• keeping task-relevant information

3.3 View Selection Influences Mutual Information and Accuracy
Example1. Reducing I(v1;v2) with spatial distance

Example2. Reducing I(v1;v2) with different color spaces

MI량뿐만 아니라 MI량의 하한도 적당하면 좋다~(?)
3.4 Data Augmentation to Reduce Mutual Information between Views
제안한 InfoMin aug 방법이 아래의 방법에서 가장 뛰어난 결과를 보인다.
• Single-crop ImageNet accuracy - 이미지 일부 잘라서 label 정답(?)
• Object Detection - 객체 위치 종류 반환
• Instance Segmentation - 픽셀 단위로 label 식별
4.1 Optimal Views on Downstream Task
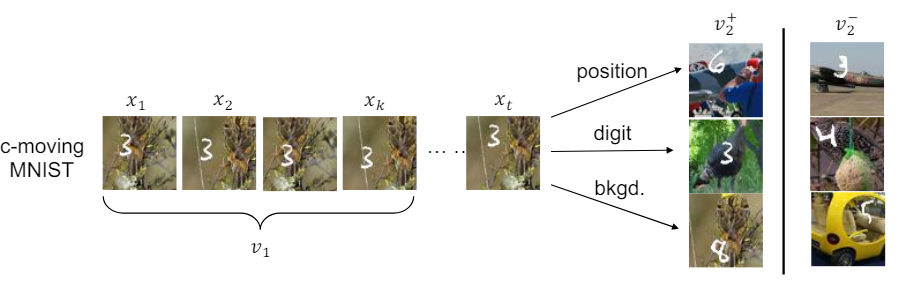

• Single Factor Shared - 하나의 변수만 고유할 때 해당 변수가 task와 관련이 있으면 성능 좋음.
• Multiple Factors Shared - 여러 변수를 공유할 때 특정 변수가 다른 변수를 압도할 수 있음. (background)
4.2 Synthesizing Views with Invertible Generators
⁕ Unsupervised View Learning: Minimize I(v1;v2)
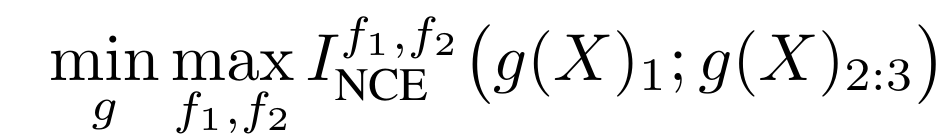
⁕ Semi-supervised View Learning: Find Views that Share the Label Information
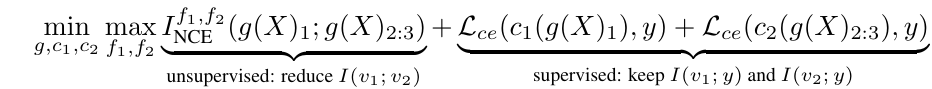
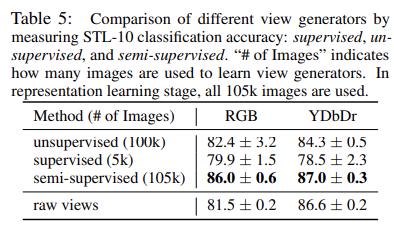
240524 10:30 미팅 기록
unsupervised learning이 추세 -> 이때 contrastive learning을 많이 함
positive sample로만 contrastive learning하는게 한계가 있음
pos 가깝게 nag 멀게
view? -> 데이터를 어떻게 처리하냐에 따라 view가 달라짐
이 논문을 보게된 배경
그래프에서 몇몇의 링크가 없어도 예측을 잘하는게 중요함
-> 특정값을 정확히 아는 것보다 distribution, 경향성을 아는 게 중요함.
-> 이 방안으로 contrastive learning
괜찮은 여러 view를 만드는 게 중요하다.
우리도 새로운 view를 만드는 것이 목표 ? -> 좋은 뷰라면 갖춰야 할 것들이 있을텐데
-> 이 논문 적합!
(+ 잘 쓰여진 논문을 보여주기 위해!!!!!)
정보 이론에서 나오는 아래의 개념은 알고 있어야 함. 아예 처음부터 예제로 이해해라
Information, Mutual Information, Entropy, Cross Entropy, KL divergence, NCE, InfoNCE
(-> 서로 다른 정보를 가지고 주고 받기위해 통신쪽에서 정보 이론을 많이 배움)
이미지 vs 그래프
이미지: 주변 픽셀의 convolution
그래프: 주변 노드의 convolution
이미지 증강: 회전, 블러, 색 변경 등
그래프 증강: 노드 피쳐에 masking과 같은 수정, 링크 제거 or 링크 추가
이 논문에서 얻어갈 것(2)
그래서 어떤 뷰가 좋은거냐!, 기본 개념들
(- log(1/n))의 형태를 많이 볼 것임
내가 내 언어로 말을해야 진정한 학습이 된다 !
오답 노트를 하느냐 안 하느냐가 중요한 것 같다!
기본 개념을 알고 논문을 다시 보고 내 단어로 정리하기. -> 짧고 내 단어로!
'연구 > 논문' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [논문정리, 미팅기록] Hard Sample Aware Network for Contrastive Deep Graph Clustering (AAAI 2023) (1) | 2024.05.29 |
|---|---|
| [미팅 후 기록] What Makes for Good View for Conrastive Learning? (NIPS 2020) (0) | 2024.05.29 |

